React.js is a JavaScript library used to create the frontend of a single-page web application. It reduces the complexity of an application by dividing the UI into small and more manageable components.
We usually create a React application using the npx create-react-app app-name command. You can learn more about creating a React app from here.
This article discusses an alternative way of setting up a React application using Vite.
We will focus on:
- Meaning of Vite.
- Benefits of Vite.
- Features of Vite.
- How to create a React application using Vite.
Prerequisites
To follow along, you need a basic understanding of:
- React.js.
- Hot Module Replacement page talks.
You should also have Node.js installed on your computer. Node provides the Node Package Manager (npm) used to configure dependencies in a React application.
What Vite is?
Vite is a build tool that promotes a faster development experience for developers. It was created by Evan You.
Vite supports the following:
1. Hot Module Replacement
A fast development server, that provides swift Hot Module Replacement (HMR), due to its enhanced features.
You can read more about ES native modules from here.
2. Rollup
Vite has a build command that bundles the developer’s code with Rollup.
This is a JavaScript module bundler that compiles simple pieces of code and builds them into complex applications.
Since Rollup is pre-configured, it’s easy to generate static applications that are highly optimized for production.
You can access more information about Rollup from here.
Benefits of Vite
A developer’s productivity is influenced by many factors including performance and speed.
JavaScript can cause an application to slow down depending on its complexity. Vite resolves this issue by using Esbuild.
EsBuild is a dependency pre-bundler that enhances the pre-bundling of dependencies than other frameworks. This results in increased server speeds and Hot Module Replacement.
Features of Vite
The key features of Vite include:
- Instant server start.
- Fast Hot Module Replacement.
- Optimized build process.
Let’s now create a React application using Vite.
Creating a react application using Vite.
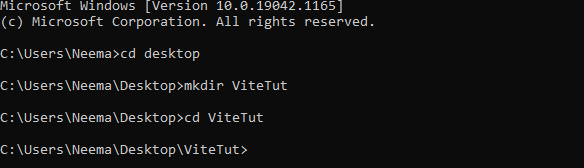
Navigate to your desktop and create a new folder. This directory will store all of our files.
Next, launch a command window and navigate to the app’s directory, as shown below:
Note that we will be using npm in this tutorial. However, if you prefer yarn, you can access it from here.
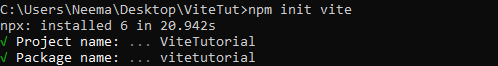
Write the following command in your CLI.
npm init vite
We need to add a project and package name, as demonstrated below:
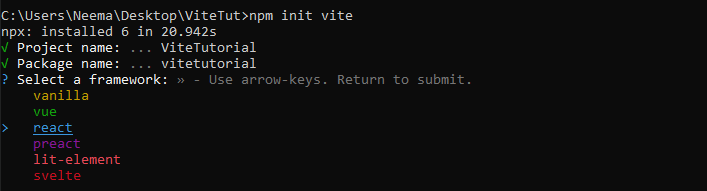
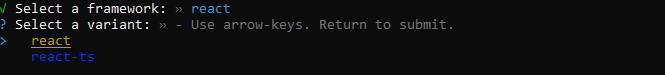
We then need to select React as the framework and variant:
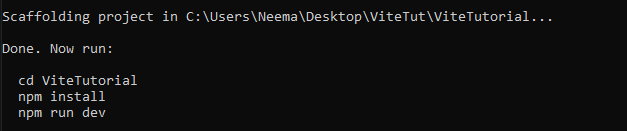
Our project is now created. Let’s install and then run it.
In the terminal, navigate into the generated project. In my case, ViteTutoral and type the command below:
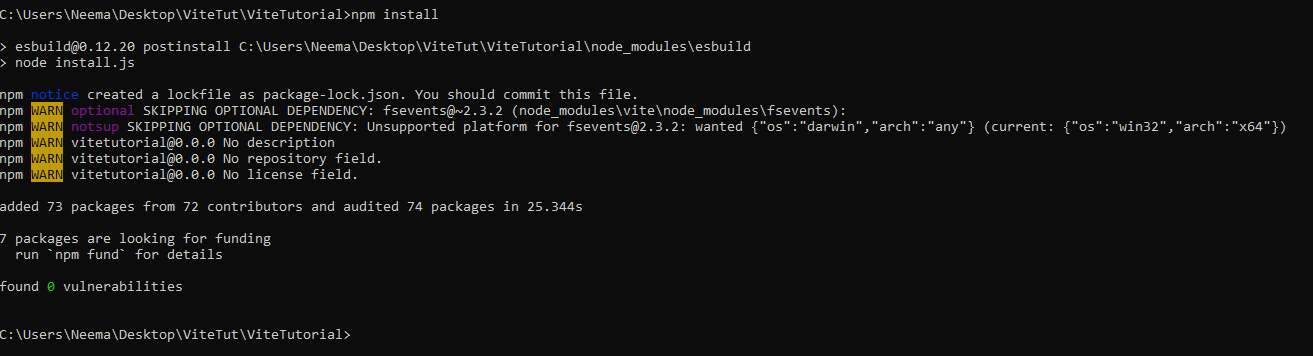
npm install
This command installs the required dev dependencies which you can access from the package.json file.
It also creates a node_modules folder which can be viewed as an external modules’ cache.
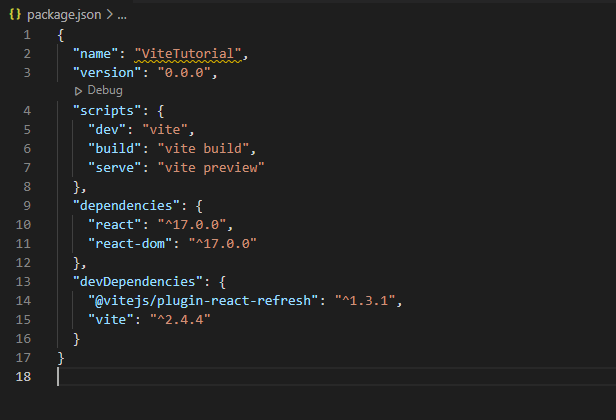
Your package.json file should look, as shown below:
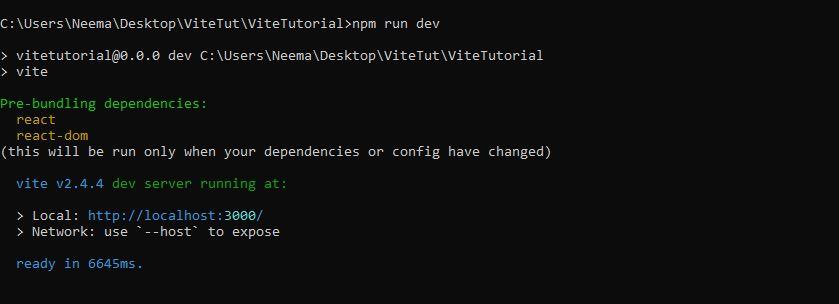
Finally, include the following command to start the dev server:
npm run dev
Copy and paste the provided link on your browser. You now have React and Vite running on your local server. Congratulations!
npm run serve command does the app build and renders the production version while npm run dev initializes the development server.
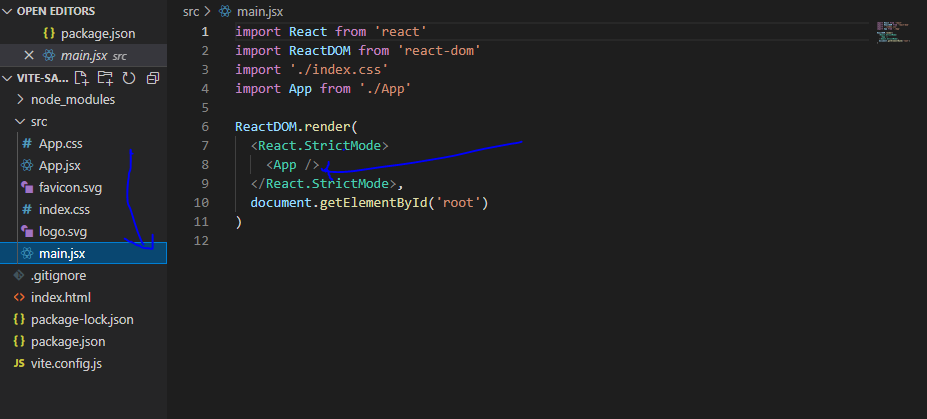
When you open the project folder in your code editor, you will see different files among which is the main.jsx file.
The code responsible for the browser’s output is in the App.jsx and is rendered from the main.jsx file.
Let’s create a simple application to learn more about Vite.
Include the code below in the App.jsx file:
import React from 'react'
import './App.css'
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Working with Vite</h1>
<p>Hello There! This was such a first fun experience creating a React app using Vite.
The lightning-fast starting of the dev server is such an amazing experience while using this tool compared to the normal<b>npx create-react-app (app-name) way.</b>
Now I will run the **"npm run serve"** command to experience the instant HMR experience that Vite provides.
</p>
<h1>Happy Coding!</h1>
</div>
)
}
export default App
Now head to your terminal and run the npm run dev command again and follow the provided local link.
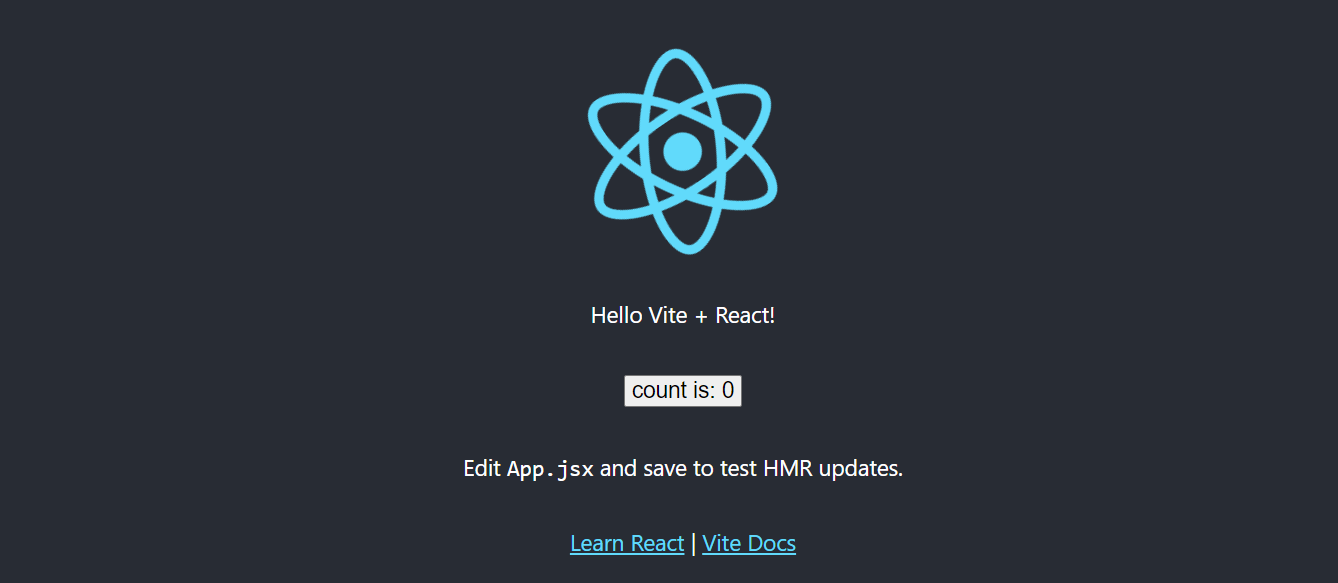
We have now created our simple React+Vite app that looks like this:

Note that in Vite, index.html file is not placed in the public folder as in React. This HTML file has a
<script type="module" src='..'></script>module which is essentially the point of entry of a React app.
You will also realize that the %PUBLIC_URL% option is missing. This placeholder maps any static files within React’s public folder.
%PUBLIC_URL% is not required in Vite due to the automatic rebasing of URLs in the index.html file.
Conclusion
This article has discussed how to create a React + Vite app using the Vite build tool. It also highlighted the features and benefits of Vite.
You can, therefore, use the knowledge and skills acquired from this tutorial to craft more quality applications.
Good luck!









Comments: