Flatologic is a company that offers free and premium dashboard templates in various frameworks. Whether in Angular, Vue or React, developers can find many user-friendly pre-built applications to suit their needs.
Rather than starting a project from scratch, this drastically reduces the amount of coding involved and gets a project running quickly.
In this tutorial, we will focus on their free template called React Dashboard. This template is built with React, Bootstrap, React Router, Redux, and GraphQL. It comes with a React frontend and a Node.js backend.
Authentication is included and the layout is responsive. This tutorial will cover how to create a dashboard in three easy steps. Then, we will connect it to an SQL database with MAMP so you have some local data.
Objectives
After reading this article the reader will be able to:
- Install and configure React Dashboard.
- Set up a React Database table and dashboard.
- Connect the database server to the application.
Prerequisites
To follow through this tutorial, you will need:
- Knowledge of fundamentals of React.
- Basic knowledge of the MAMP Server.
Let’s get to it!
Step 1: Setting up the React Dashboard project
To start with, let’s clone the React Dashboard repository and choose a name for our new project. This will be executed using the following command:
git clone -o React Dashboard -b master --single-branch https://github.com/flatlogic/React Dashboard.git <app-name>
Once the project is cloned on our local machine, we can proceed with installing the required dependencies.
cd <app-name>
yarn install
At the time of writing, React Dashboard runs into an issue when you run yarn install and there is a GitHub issue logged. Here is a snippet of the error:
error /Users/..../node_modules/sqlite3: Command failed.
Exit code: 1
Command: node-pre-gyp install --fallback-to-build
If you run yarn add sqlite3 separately and then re-run yarn install, things should work fine.
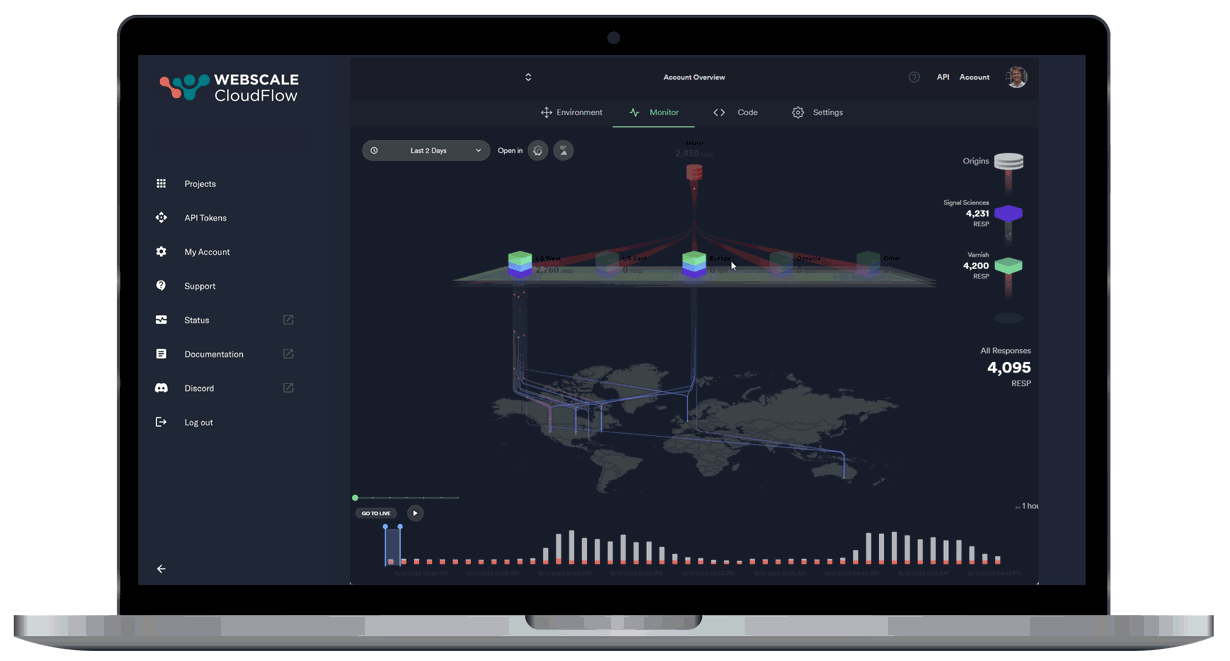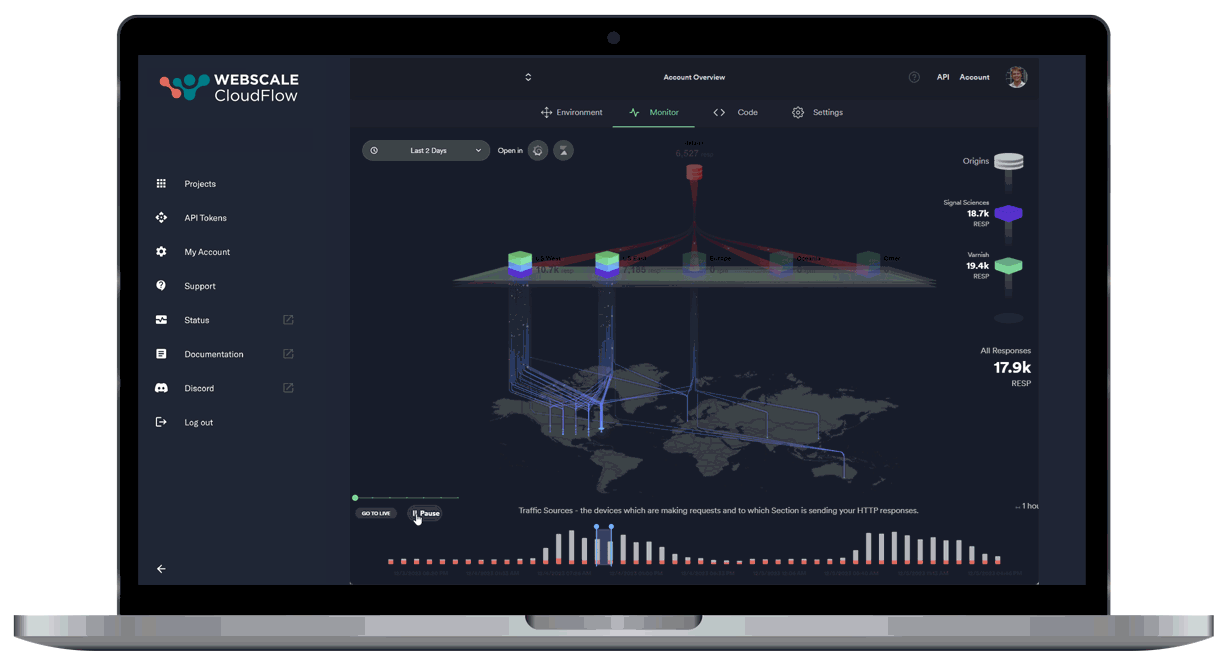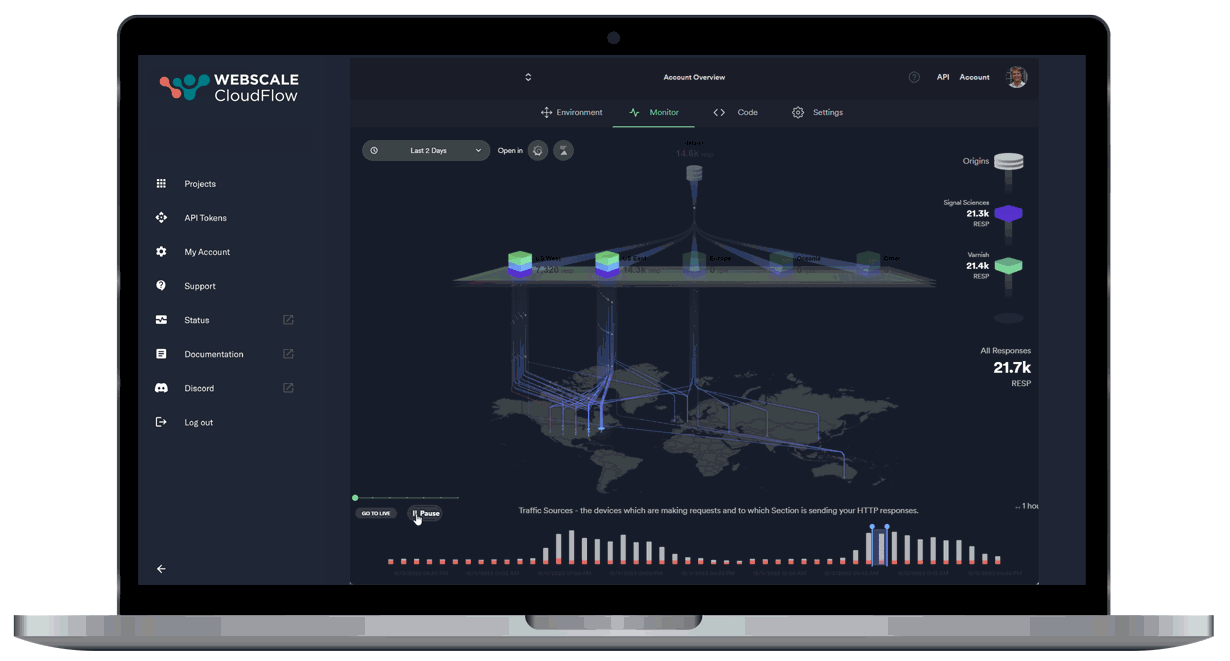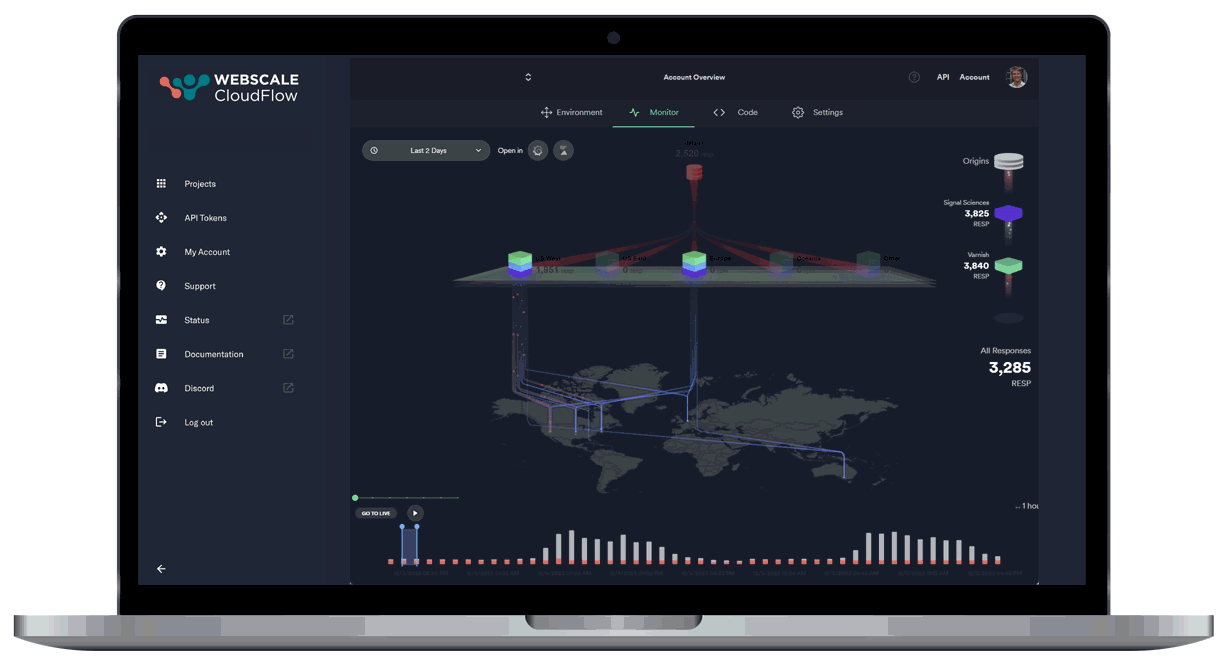
Afterwards, run yarn dev. This will launch the backend and frontend servers, which will be accessible on ports 5000 and 3000, respectively. If you navigate to http://localhost:3000/, you should see the dashboard:
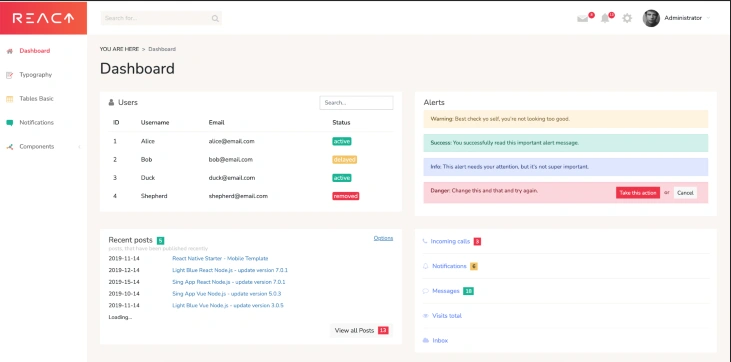
This project also comes with GraphQL. Once the app is launched, the playground is accessible at http://localhost:5000/graphql. If you are unfamiliar with this technology, do not hesitate to read the GraphQL documentation and learn how to create queries and mutations.
Step 2: Creating the dashboard and table
We have a great dashboard, but at the moment, it is working with hard-coded values. To make it more valuable, let’s connect our new application to a local database.
You can choose any database, but for the sake of this tutorial, we will connect a MySQL database.
To create one, we will use MAMP, which allows us to get Apache, Nginx, PHP, and MySQL out of the box.
If you do not have MAMP, you can download it here. After installing, start the application and click Webstart.
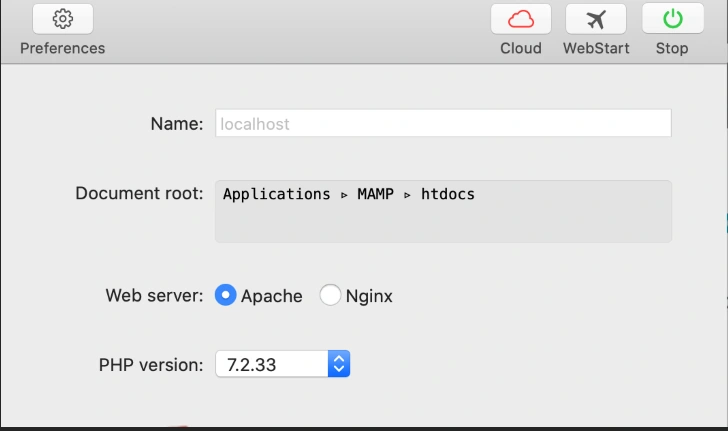
The Webstart tab opens the MAMP index page at http://localhost:8888/MAMP.
On this page, you will see plenty of information, but what we care about is under MySQL. Once opened, click on phpMyAdmin. This will open another tab, this one to http://localhost:8888/phpMyAdmin/index.php, where you will see the interface of phpMyAdmin.
Thanks to this, we will be able to see, create, and work with our future MySQL databases. We can create a database by clicking on Databases. Then, enter the name of our new database and click Create.
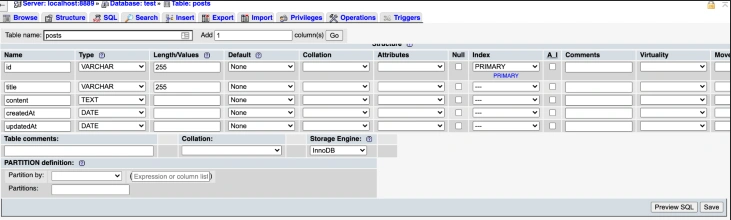
We may then create our first table. For our tutorial, name it posts and select five columns, as we will have five fields. Once we click Go, we will be able to add new fields.
Our fields should be as such:
- ID of type varchar; length 255 is our primary key
- title of type VARCHAR; length 255
- content of type TEXT
- createdAt of type DATE
- updatedAt of type DATE
Below is a screenshot of our table with our new fields:
After adding all the required information, click on Save.
Step 3: Linking the local database to your application
This project uses Sequelize, a Node.js ORM that allows you to connect to SQL databases. In our data folder inside src, we find a sequelize.js file where we can connect our database.
We will connect the database with Javascript, as shown below:
import Sequelize from "sequelize";
// Configure the connection to your local database with your DB name, username, password and the port on which your DB runs.
const sequelize = new Sequelize("test", "root", "root", {
host: "localhost",
port: 8889,
dialect: "mysql",
operatorsAliases: false,
});
export default sequelize;
Then, in the same folder, open the schema.js file and uncomment the mutation for post creation. This will allow us to create new posts in our database from our frontend.
Note: Once again, if you are unfamiliar with the concept of mutation, check out GraphQL’s documentation.
import {
GraphQLSchema as Schema,
GraphQLObjectType as ObjectType,
} from "graphql";
import me from "./queries/me";
import news from "./queries/news";
import posts from "./queries/posts";
import addPost from "./mutations/posts";
const schemaConfig = {
query: new ObjectType({
name: "Query",
fields: {
me,
news,
posts,
},
}),
};
// If you want to enable mutation, uncomment the code below
schemaConfig.mutation = new ObjectType({
name: "Mutation",
fields: {
addPost,
},
});
const schema = new Schema(schemaConfig);
export default schema;
Step 4: Testing the application
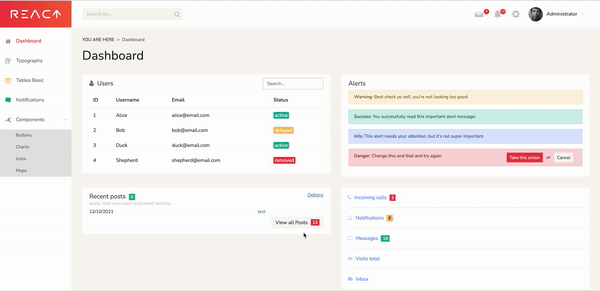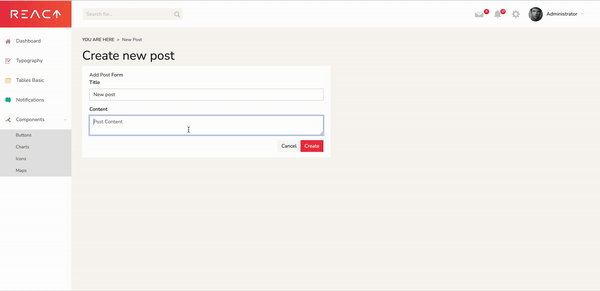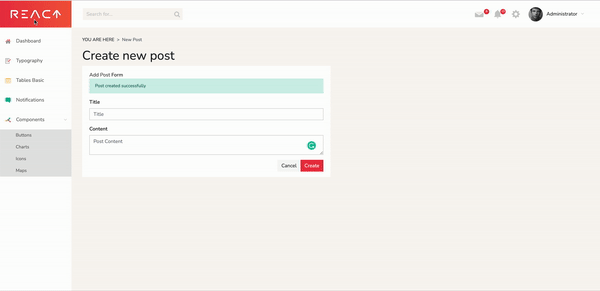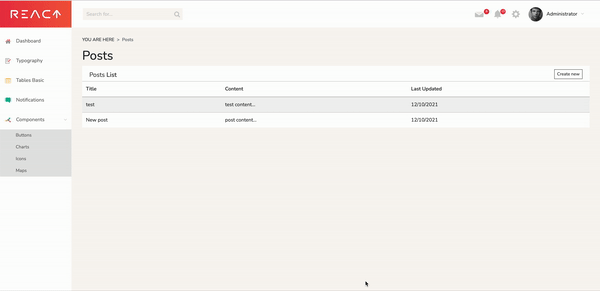
Kill the server with Cmd+C and start it again. If everything worked, we should be able to create new posts.
In our dashboard, we can click on View all Posts, then Create New. After we input a title and content, we can click Save. When we go back to the dashboard page, our new post will appear in the table.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we learned how to clone the React Dashboard template from Flatologic and launch it locally. This allowed us to have a user-friendly dashboard up and running quickly.
Then, we created a MySQL database with a table and some fields and connected it to our new application. Thanks to this pre-built dashboard, developers around the world can quickly build a React application.
Starting a project from scratch can be time consuming but these templates come with all the functionalities needed to get started and will have you save time and effort.
Happy coding!









Comments: